About Breast Reconstruction » Implant Procedures » Tissue Expander to Implant Procedure
Tissue Expander to Implant Procedures
On this page

On this page
Implant breast reconstruction may require the use of tissue expanders. A tissue expander is a temporary adjustable implant with a built-in port to inject air or fluid.
Expanders are used to stretch the skin at the breast site before placing an implant. An expander may also be used if there is concern about blood supply to the skin, to prevent tension or weight on the skin until it has healed. Finally, expanders can be used to better position the implant pocket prior to placing the final implant. The most common procedure that uses tissue expanders is known as expander-implant reconstruction.
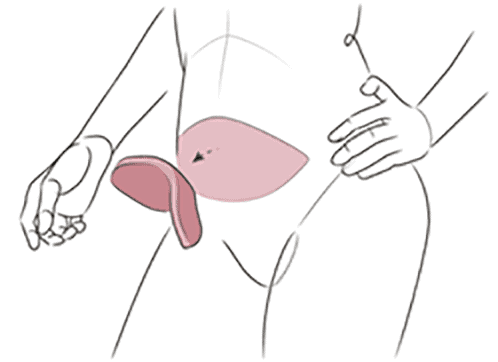
How Tissue Expanders Work
Breast Reconstruction with Tissue Expansion – “Expander to Implant”
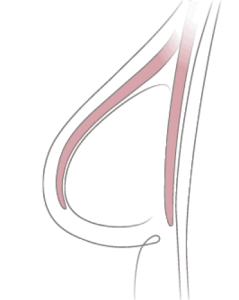
If a large amount of skin was removed during the mastectomy, or if you would prefer a larger breast, then it may be necessary to stretch the skin and the chest muscle at the site of the new breast. In this case, a tissue expander — an adjustable implant that contains a built-in injection port—is inserted under the breast skin, either beneath or on top of the chest muscle. This technique is called two-stage reconstruction. There may also be a third stage, in which the nipple and areola are reconstructed or additional enhancement procedures are performed.
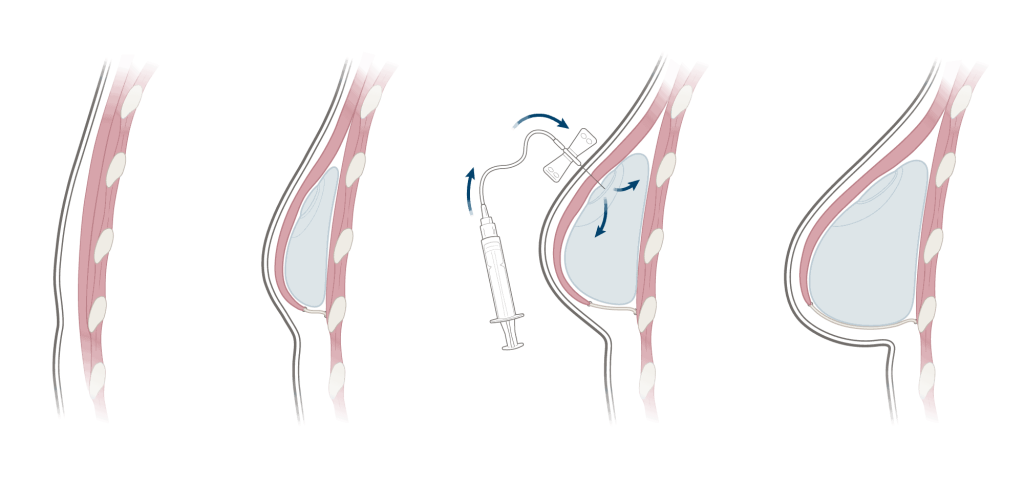
Procedure
Expander-Implant Reconstruction
Expander-implant reconstruction is considered a two-stage or delayed immediate reconstruction. Although the reconstruction process begins at the time of mastectomy with the placement of tissue expanders, the final implant placement takes place during a second, separate surgery.
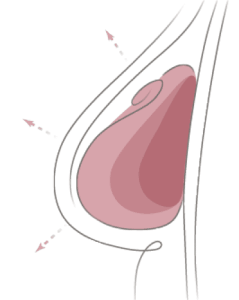
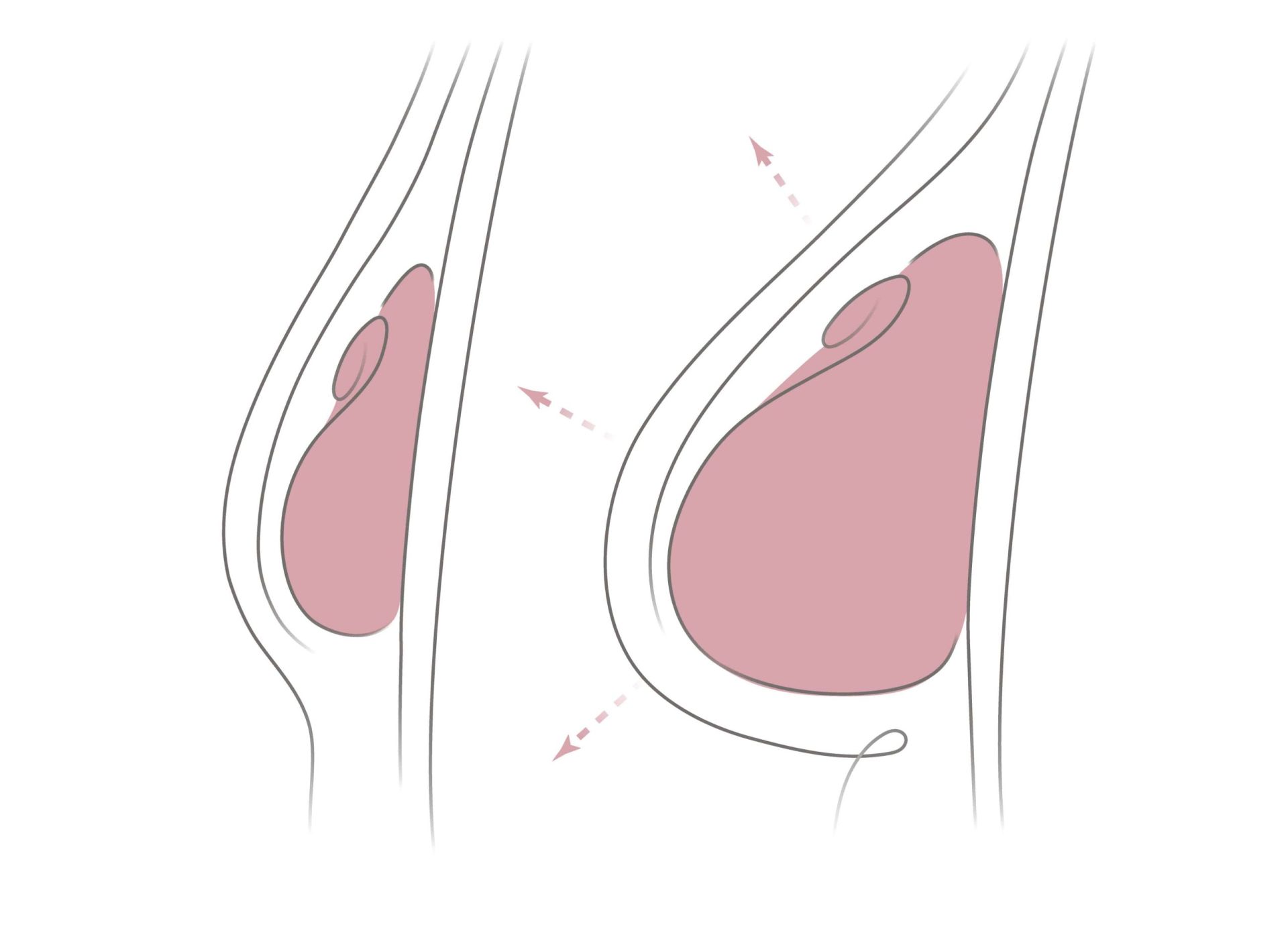
After the placement of the tissue expanders, a small amount of saline will be filled into the expander during the initial surgery. Over a period of several months, your surgeon will add increasing amounts of saline to the tissue expander through the port, allowing for the skin and muscle to stretch and expand gradually over time. The time of expansion varies depending on desired volume and breast size, but it can take a few weeks to a few months to achieve. You can expect that process typically takes 2 to 3 months to be fully expanded at 1-2 week intervals, starting approximately 7-14 days after the initial surgery. The “fills” are done in the office setting and takes no more than a few minutes to perform.
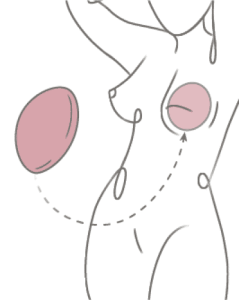
When the skin and muscle have stretched enough to accommodate the implant, the expander is removed and the permanent implant is inserted. The Stage Two surgery, often referred to as the “exchange surgery,” typically takes 2-3 hours to perform and patients leave the hospital the same day. Having chemotherapy or radiation therapy can affect when the permanent implant is inserted, so you’ll need to discuss timing with your doctor.
Stage Three reconstruction, in which the nipple and areola are reconstructed, generally happens 2-4 months after placement of the permanent implant. Fat grafting is also sometimes performed as an additional procedure to help fill and contour the breast and achieve optimal results.
Delayed Reconstruction with Tissue Expansion
Implant surgery can also be done some time after the mastectomy and treatments. A tissue expander can be inserted 4-6 months after your last treatment. Tissue expansion can even begin years after the mastectomy, depending on the condition of your skin at the breast site—how much skin has been preserved and the amount of scarring.
Recovery Time
Recovery time for implant reconstruction is usually shorter than that for flap reconstruction. You’ll probably be able to return to your usual activities in about 4-6 weeks. If you have a tissue expander removed and replaced with a permanent implant, recovery will take about 2 weeks.
Additional Procedures
- If the nipple and areola are not preserved during your mastectomy, you may choose to have nipple and areola reconstruction as a third-stage procedure. This procedure usually takes place 3-4 months after placement of the permanent implant.
- Additional cosmetic procedures including fat grafting and liposuction can be performed to improve symmetry and appearance.
Things to Consider
- The use of tissue expanders can increase the overall length of the reconstruction process.
- You will probably need tissue expanders if you choose delayed reconstruction or if you have already had your mastectomy.
- Tissue expanders may allow for larger breast volume than DTI (direct-to-implant) reconstruction.
Additional Choices and Alternatives
Timing of your implant procedures is an important consideration in breast reconstruction. If your implant reconstruction does not require tissue expanders, you may be able to have your implants placed at the same time as your mastectomy.
You and your surgeon will also need to determine whether implants should be placed above the pectoral (chest wall) muscle or below it.