Placeholder
About Us
Breast Cancer
Breast Reconstruction
Prep, Recovery & Support
Placeholder
Tab Content
About Us
Plastic Surgeons
Breast Surgeons
Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Treatment
Lymphatic Surgery
Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction
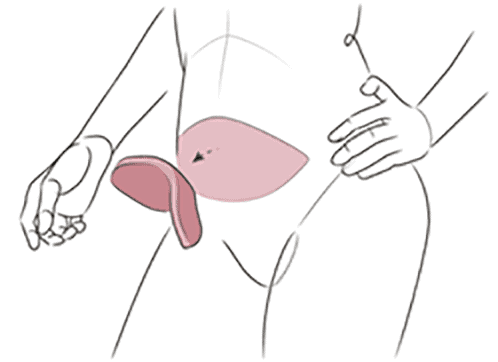
Abdominal Natural Tissue (Flap)
Alternative Natural Tissue (Flap)
DIEP Flap Procedure:
Advanced Natural Tissue Reconstruction
Innovative microsurgical and robotic techniques that produce natural-looking results.
Prep, Recovery & Support