About Breast Reconstruction » Natural Tissue (Flap) Reconstruction » Abdominal Tissue Site » DIEP Flap Procedure
The DIEP Flap Procedure
On this page

On this page
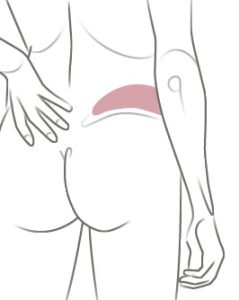
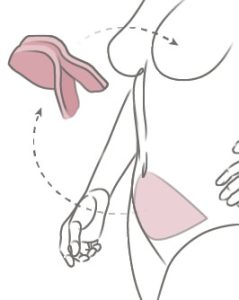
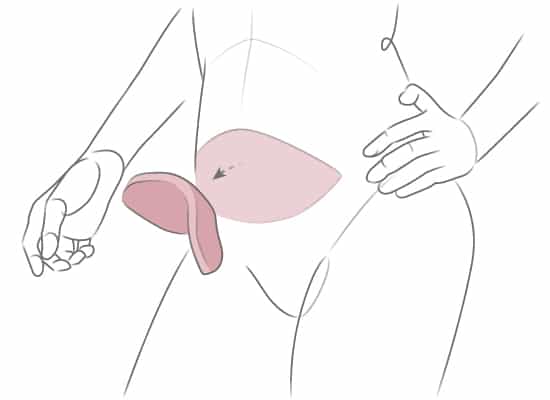
The DIEP flap is the most common tissue flap procedure performed at the Friedman Center due to its natural-looking results. In the DIEP procedure, a flap of tissue containing fat and skin is removed from the lower abdomen and used to form a new breast.
Unlike TRAM flap surgery, another abdominal flap procedure, DIEP flap surgery preserves the abdominal muscles. Because the new breast is made entirely of living abdominal tissue, which is similar to breast tissue in appearance and texture, the new breast looks and feels soft, warm, and natural. After surgery, many women enjoy having a flatter abdomen, similar to the effects of a “tummy tuck.”
Procedure
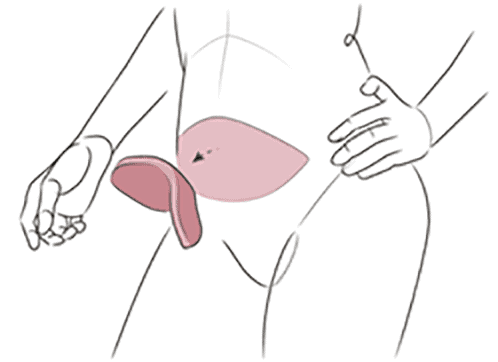
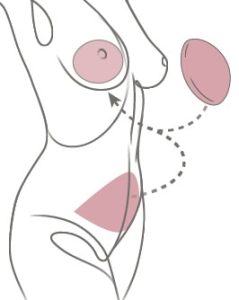
In most cases, the DIEP surgery can be done on the same day as the mastectomy (immediate reconstruction). If you’ve already had a mastectomy, the DIEP can be at a later date (delayed reconstruction). During the procedure, a flap—a piece of tissue containing skin, fat and blood vessels—is removed from the lower abdomen, below the belly button, and transplanted to the chest.
The DIEP procedure is named after the blood vessels that nourish the fat and skin of the lower abdomen, the deep inferior epigastric perforator vessels, which travel through the abdominal muscles. Very small incisions are made through the muscle to access these vessels, which are reconnected to the new blood supply in the chest. Sometimes it’s necessary to remove a small piece of cartilage from the chest to access the vessel. Using microsurgery, the plastic surgeon connects the tiny blood vessels in the chest to the vessels in the flap. The flap is then shaped to create the new breast.
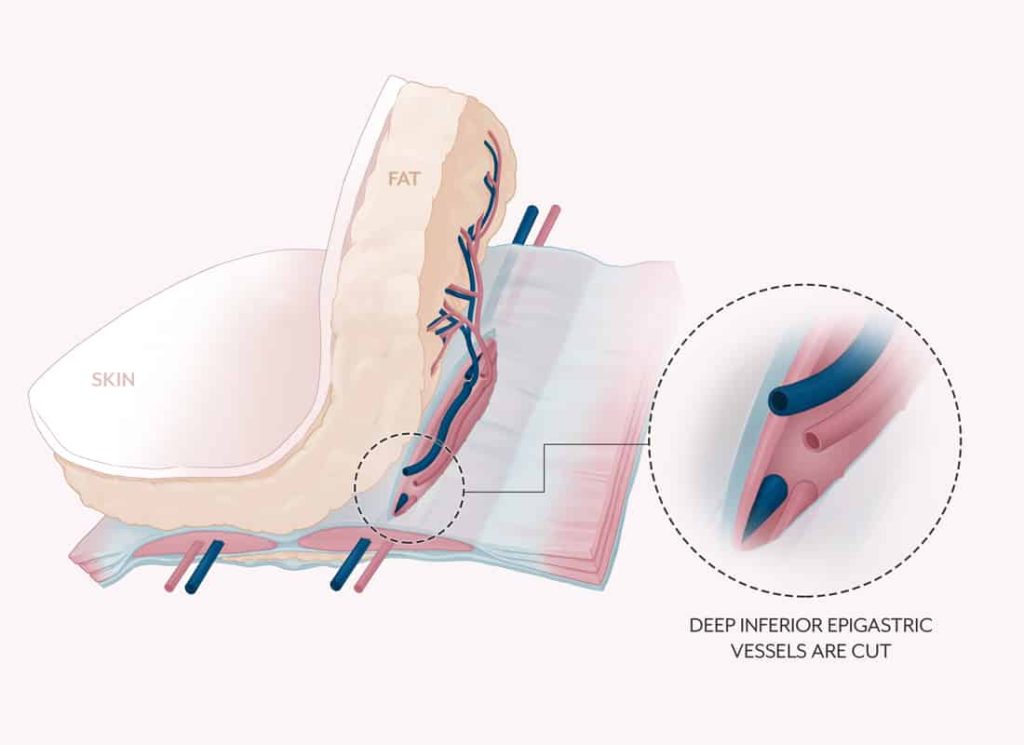
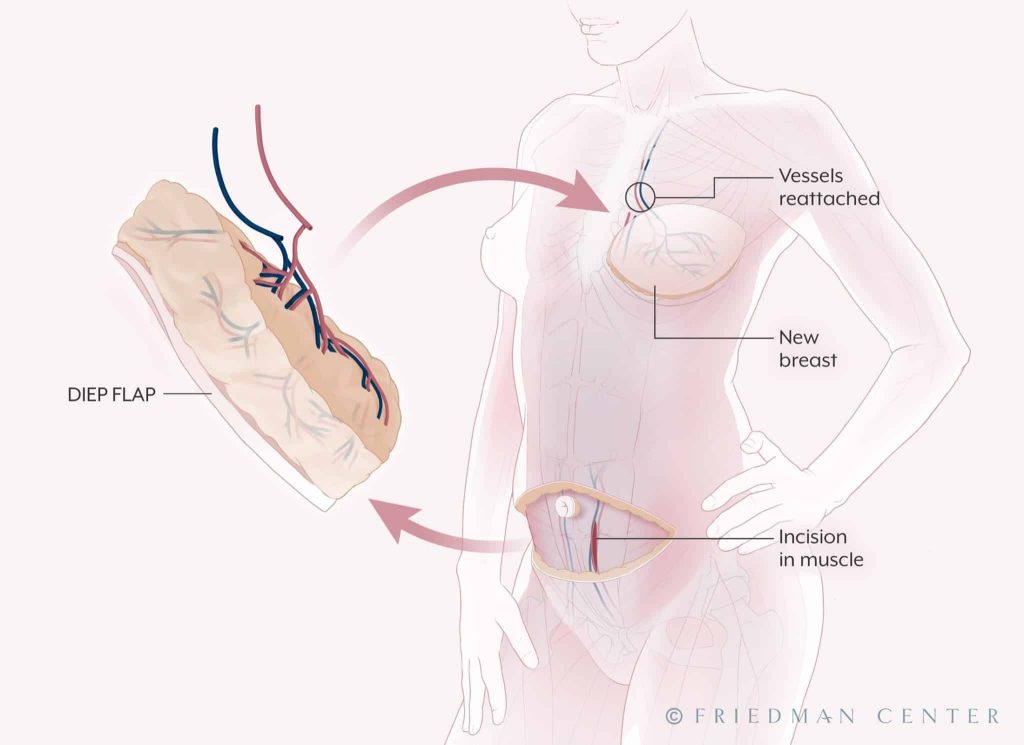
The Friedman Center is now performing robotic surgery for DIEP flap procedures
Your Recovery
Recovery Time
The usual hospital stay for a DIEP flap procedure is 1-3 days. You’ll be able to return to most activities after 6-8 weeks, but no heavy lifting may be done for 6-12 weeks after surgery. It can take up a year for your tissue to completely heal.
Expect to Feel
Expect soreness, swelling, and bruising at all surgery sites, including the abdomen. You might experience some loss of sensation, which is often temporary at the donor tissue site.
Because DIEP flap surgery preserves the abdominal muscles, patients have better outcomes than with TRAM flap procedures: you’ll retain more core strength, feel less pain, have lower risk of abdominal hernias, and recover more quickly.
Scarring
The abdominal incision for the DIEP flap procedure runs horizontally from hip bone to hip bone across the lower abdomen, about a third of the way between the top of your pubic hair and your belly button. The scar may be higher than a tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) scar, but it often sits under the bikini line. Although the DIEP flap scar is long, it typically fades over 12-18 months. Your breast scars will largely depend on the type of mastectomy you end up having
Additional Procedures
DIEP flap reconstruction can often benefit from minor “touch-up” or enhancement procedures, which are usually performed in an outpatient setting a few months after the initial surgery.
If you did not have a nipple-sparing mastectomy and wish to have nipple reconstruction, that procedure also takes places once healing from your DIEP flap procedure is complete.
Things to Consider
- If you’ve had prior abdominal surgery, you may not be a candidate for breast reconstruction using abdominal tissue.
- After flap reconstruction, the new breast made of living tissue becomes part of your body, while implant reconstruction involves a synthetic implant that will eventually need to be replaced.
- Tissue can be taken from your abdomen for breast reconstruction just once. If you have a second mastectomy, the tissue will need to come from your buttocks or your back.
- After breast reconstruction, you’ll have little to no sensation in the breast. You’ll also have less sensation in the area around the abdominal incision after the DIEP procedure.
Contraindications and Alternatives
Each donor tissue site has its own set of contraindications. Previous surgery or tissue damage may rule out one or more donor sites for breast reconstruction. Women who are very thin may not have enough tissue to make certain donor sites viable, although stacked flap or hybrid procedures can be good alternatives in those situations.
In general, the abdomen is the preferred donor site for flap reconstruction, usually through the DIEP flap procedure. The abdomen typically provides ample tissue for reconstruction and offer the same result as a “tummy tuck” as an added benefit.