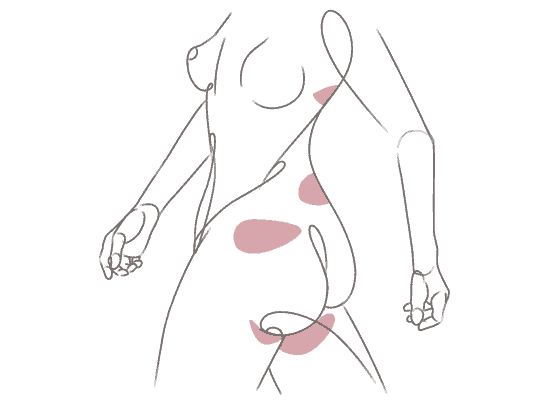About Breast Reconstruction » Natural Tissue (Flap) Reconstruction
Natural Tissue (Flap) Reconstruction
On this page

On this page
Natural tissue (flap) reconstruction uses tissue from another part of your body to form the new breast. The flap, which includes skin, fat, and sometimes muscle, is surgically removed from the abdomen or from alternative donor sites, such as the back, buttock or thigh.
Since the breast is formed from your own tissue, and it looks, feels and behaves like a natural part of your body. Tissue flaps are often used by themselves to reconstruct the breast. In some cases, when there is not enough tissue, a flap can be combined with a breast implant to create more volume or projection.
At the Friedman Center, our surgeons specialize in the DIEP flap procedure, a highly specialized type of flap reconstruction that takes tissue from the abdomen. The DIEP flap offers women the benefit of a “tummy tuck” in addition to their new breasts.
In general, flap procedures are longer surgeries that require more recovery time than breast implant procedures. However, natural tissue reconstruction lasts for life. Implants can rupture, and eventually all implants need to be removed and replaced at the end of their lifespan.
The Most Natural Look and Feel
Using your own tissue for breast reconstruction provides the most natural look and feel of any type of breast reconstructive surgery. Unlike breasts formed with implants, breasts made from natural tissue are warm and soft. They even behave like your own body—for example, the reconstructed breast will increase and decrease in size as you gain and lose weight. Click here to compare natural tissue vs. implant reconstruction.
TYPES OF TISSUE FLAP SURGERY
Different Types of Flap Procedures
There are two different types of flap procedures: free flap and pedicled flap.
Free Flap
In a free flap procedure, the tissue flap is completely separated from its original blood vessels and connected to a new blood supply in the chest. Free flap breast reconstruction requires microsurgery, which is done using a microscope. Tiny, microscopic blood vessels must be surgically connected to nourish the new breast with an adequate supply of blood. Most natural tissue procedures use the free flap method, which must be performed by highly specialized plastic surgeons.
The DIEP flap, which takes tissue from the abdomen to rebuild the breast, is one of the most advanced free flap procedures. The Friedman Center’s surgeons specialize in reconstruction using the DIEP flap and can perform this advanced surgery using revolutionary robotic technology.
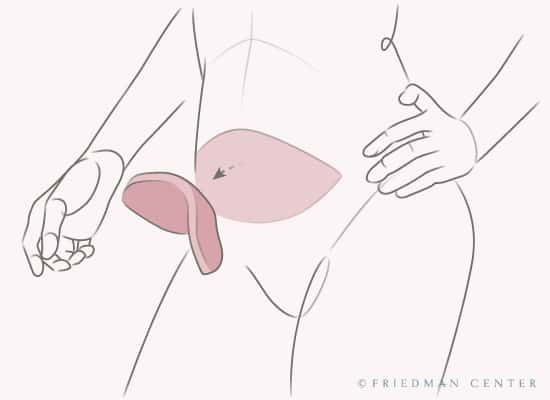
Pedicled Flap
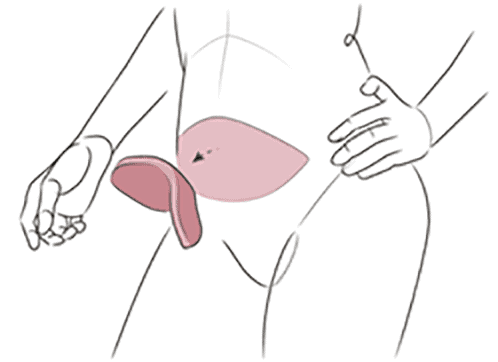
In a pedicled flap, the tissue remains attached to its original blood vessels and is tunneled under your skin to the breast area. In both types of flaps, the tissue is formed into the shape of a breast and stitched into place.
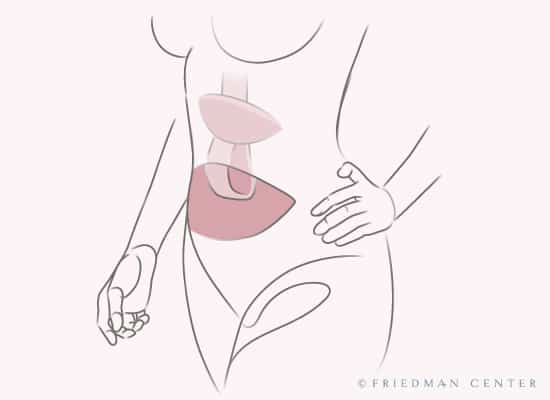
Donor Tissue Sites
The most common flap procedures use tissue from the abdomen for breast reconstruction. At the Friedman Center, we often recommend the DIEP flap procedure because of its advanced microsurgical approach.
For some patients, however, the abdomen may not be the best donor site. Alternative tissue sites for flap reconstruction include the buttock, thigh, or back.
Stacked flap procedures, which combine abdominal tissue with tissue from a second donor site, are another option.
The Friedman Center is now performing robotic surgery for DIEP flap procedures
Recovery Time
Recovery from flap reconstructive surgery can take anywhere from several weeks to several months. The time needed for recovery varies from patient to patient, depending on the patient’s general health and level of physical activity. Most patients can return to work in 3-4 weeks and resume light exercise by 6 weeks. Complete healing can take from several months up to a year.
Additional Surgery
Additional (stage 2) surgery may be needed after the initial surgery to make your breasts as symmetrical as possible. Fat grafting (also called lipofilling) may be performed to give the breast a more natural appearance. Cosmetic sculpting procedures are usually far less invasive than the initial surgery. They’re often same-day surgeries and typically have much shorter recovery times.
Do you prefer to use your own tissue for reconstruction?
You may be a good candidate for flap reconstruction if you:
Prefer to use your own tissue instead of an implant
Are not a candidate for implant reconstruction
Have had failed implant reconstruction
Have had radiation to your chest wall
You may not be a good candidate for flap reconstruction if you:
Lack enough tissue to restore the missing breast tissue (in this case, you may want to consider hybrid breast reconstruction)
Have undergone certain abdominal procedures such as an abdominoplasty
Have a history of blood clots or clotting disorders

See the difference between natural tissue and implant reconstruction.
Things to Consider
Partial breast reconstruction after lumpectomy may be a good option for you if you have early-stage cancer, particularly if only a small amount of tissue must be removed. It is a good option for many patients as it preserves the nipple and sensation. Many types of partial breast reconstruction surgery are relatively minor. Recovery times are often shorter than for complete breast construction after mastectomy.
However, many women who are candidates for a lumpectomy decide instead to have a mastectomy with full breast reconstruction. There may be a number of reasons for this choice:
Lumpectomy is usually accompanied by radiation treatment. Radiation damages the skin and underlying tissue and may cause harmful side effects and long-term problems. With a full mastectomy, radiation treatment is often unnecessary.
After a lumpectomy, ongoing surveillance (such as MRIs, ultrasound and breast exams) is required. Some patients prefer to avoid the stress associated with ongoing exams and potential biopsies.
Partial breast reconstruction options are dependent upon each individual patient’s body, patient’s desired outcomes, and breast cancer characteristics. Oncoplastic surgery ideally should be performed at the time of lumpectomy, or shortly thereafter, before a patient receives radiation.
Many patients assume that their insurance will not cover reconstructive surgery on the unaffected breast, however, federal law requires insurance to cover all stages of breast reconstruction, including procedures to achieve symmetry of the other breast.