About Breast Reconstruction » Implant Procedures
Implant Procedures
On this page

On this page
Breast implant reconstruction uses silicone shells filled with saline (salt water) or silicone gel to create volume in the new breast. This type of reconstruction procedure requires less surgery than Natural Tissue (Flap) reconstruction, since it only involves the chest area and eliminates a tissue donor site.
Microsurgery isn’t required, so the operation takes less time and the recovery time is usually shorter.
Implant reconstruction, like natural tissue reconstruction, can be done at the time of the mastectomy, or it can be started at that time and completed later. Implant reconstruction may require additional surgery in the future, as implants are recommended to be changed out after 10-20 years, depending upon the type of implant used.
Implants may be a good option for thin women who do not have enough extra tissue on their bellies, backs, thighs, or buttocks to consider natural tissue reconstruction. However, some of the newer advanced microsurgical procedures such as stacked flaps (using multiple layered flaps) and hybrid reconstruction (using natural tissue with an implant) have begun to address this challenge in thin women who still wish to use natural tissue for their breast reconstruction.
There are a number of factors you need to understand and consider as you and your surgeon decide which type of breast reconstruction is best for you.
Advantages and Limitations of Implant Reconstruction
There are a number of advantages to implant reconstruction:
- Does not require microsurgery. Therefore, it is a shorter, less complex surgery than natural tissue procedures like the DIEP flap.
- Desired size and shape can be discussed, as implants come in many different sizes, shapes and volumes.
- Since tissue isn’t taken from a donor site in your body, recovery is faster than with flap reconstruction.
- Implants are easy to remove and to replace if there are complications or if you want to change the size and/or shape of your breast.
- Unlike flap reconstruction, which creates scars in at least two sites in your body, implant reconstruction creates less scarring as scars are limited just to the breast area.
- Gaining or losing weight won’t change the size of the reconstructed breasts.
- Implant reconstruction can sometimes be completed in one step without the use of a tissue expander, called “direct to implant.”
Implant reconstruction also has limitations:
- A breast created with an implant feels less natural than one made with living tissue. It’s less mobile, as well as firmer and colder to the touch, than a natural-tissue breast.
- The opposite healthy breast often needs surgery to match the implant.
- If you need radiation therapy, there is a high chance of developing problems in an implant reconstruction.
- The implant may need to be removed or replaced for a number of reasons. Complications can include implant rupture, infection, and capsular contraction. There can be cosmetic problems as well, such as when the implant changes position or when ripples—visible folds or wrinkles—form in the implant under your skin.
- Up to 50% of women who have breast implants need to have the implants removed or replaced in 8-10 years because of complications.
- Implants do not last a lifetime. They typically wear out after a period of 10-20 years and may need to be surgically replaced.
See the difference between natural tissue and implant reconstruction.
Different Types of Breast Implants
There are many types of breast implants available. Each type of implant has a distinctive look and feel. Your plastic surgeon can help you choose the right implant based on the contour of your breast area and your unique aesthetic goals.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing a breast implant:
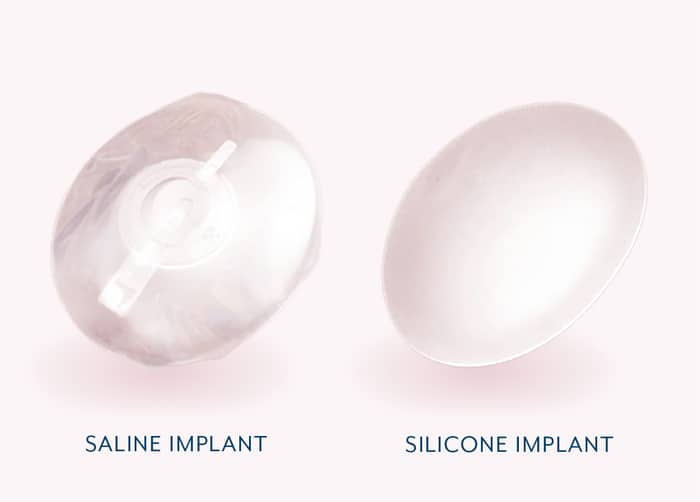
Material
- The implant has a silicone shell that is filled with salt water.
- The implant is inserted while empty and then filled with a saline-filled syringe, making placement easy.
- Saline implants have a watery, less natural-feeling texture and are more prone to rippling.
- If a saline implant ruptures, the salt water will be absorbed by the body.
- The implant has a silicone shell that is filled with silicone gel.
- Silicone implants feel more like natural human breast tissue.
- Follow-up imaging is recommended 3 years after implant placement and every 2 years thereafter.
- If a silicone implant ruptures, it should be removed to prevent migration of the silicone.
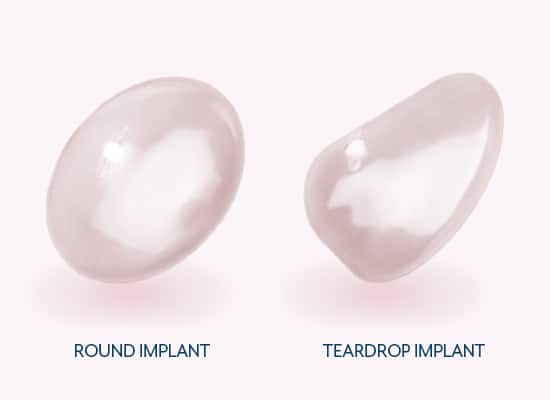
Shape
- Round implants have a spherical appearance.
- They are an excellent choice if you want a fuller appearance toward the upper region of the breast.
- Round implants are soft and typically smooth in texture.
- Teardrop implants are also known as “anatomical” implants because they provide a more natural silhouette.
- The bottom of the implant is larger than the top.
- Teardrop implants are typically made of firmer silicone and are textured, allowing them to hold their shape and stay in place.
Texture
Smooth
Textured
- Smooth implants do not attach to the body and are designed to move freely.
- A smooth surface is more common with round implants.
- A textured implant feels “pebbly” and is designed to maintain the position of the implant in your body.
- A textured surface is more common with teardrop implants.
- Due to concerns with BIA-ALCL, the Friedman Center is not currently using textured implants for breast reconstruction.
Consistency
Saline
Silicone
- Saline implants have the same consistency as water; however, they feel firm to the touch.
- Silicone implants feel soft in squishy and come in choices that are soft, medium and firm.
Size & Profile
Implants come in a range of sizes (overall breast volume) and profiles (how much an implant projects forward from the breast wall while standing). Your plastic surgeon will learn your personal preferences and help you choose an implant size and profile that gives you the best aesthetic outcome.
Placement
Implant Shape
Implant Consistency
Timing of Your Implant Reconstruction
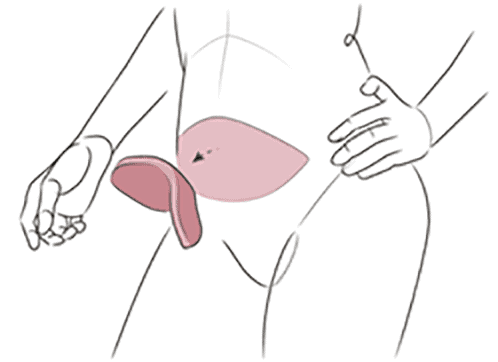
Implant breast reconstruction may be done at the time of the mastectomy without first implanting a tissue expander. This is called direct-to-implant (DTI) reconstruction. This technique is usually used for smaller breast reconstructions and still may require additional procedures to optimize the aesthetic outcome.
If the skin at the breast site needs to be stretched before an implant can be put in, then a tissue expander ( an adjustable implant with a built-in port to inject air or fluid) is first inserted to prepare for a later implant. An expander may also be used if there is concern about blood supply to the skin to prevent tension or weight on the skin until it has healed. Because expanders have tabs that can secure them in position, they may also be used to better position the implant pocket prior to placing the final implant. This technique is called two stage or expander- implant reconstruction.
Implant reconstruction can also be done well after the mastectomy, called delayed implant reconstruction, and almost always requires initial placement of a tissue expander before placing the implant.
Breast Implant Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL)
Due to the rising concern over the association of certain types of textured implants with an increased risk of BIA-ALCL, a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (cancer of the immune system), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has requested a box warning on implant packaging for textured breast implants. Although the risk of developing BIA-ALCL is thought to be low, occurring in less than 0.03% of patients, this could potentially be a serious condition if not diagnosed early or not treated promptly.
Breast implant manufacturer, Allergan, has notified the FDA that it has recalled its BIOCELL textured breast implants and tissue expanders from the global market. These products have the same BIOCELL textured surface (shell), which is a unique surface used only by Allergan. Our office has taken extreme caution and no longer uses these types of textured implants. If you have already had breast reconstruction and are unsure if you have these types of implants, call your physician. If you currently have BIOCELL textured implants, you may be a candidate for revision surgery.
Recovery
Recovery time for implant reconstruction is usually shorter than that for flap reconstruction. You’ll probably be able to go back to your usual activities in about 4-6 weeks. If you have a tissue expander removed and replaced with a permanent implant, recovery will take about 2 weeks.