Glossary of Terms
Breast reconstruction is a complex process, but it doesn’t have to be confusing. You can use this glossary of terms to learn more about the various aspects of reconstruction.
JUMP TO:
JUMP TO:
Abdominal Flap Reconstruction
A type of natural tissue reconstruction that uses the abdomen as a donor site to recreate a breast. DIEP flap, SIEA flap, TRAM flap, and (potentially) stacked flap are abdominal flap reconstruction procedures.Acellular Dermal Matrix (ADM)
Purified collagen that is often used as a sling to help hold an implant in place following breast reconstructive surgery. It can also be used in conjunction with natural tissue reconstruction for added volume and projection. The use of ADM can be a good option for women who don’t have enough natural tissue but want added projection without the use of implants.Adjuvant Therapy
Cancer treatment, such as radiation or chemotherapy, that is given after breast surgery (lumpectomy or mastectomy).Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL)
A type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, or cancer of the immune system.Areola
The round, pigmented area on the breast that surrounds the nipple.Autologous Flap
See Natural Tissue ReconstructionAxilla
The armpit region and an area with a significant number of lymph nodes.Axillary Dissection
The surgical removal of multiple lymph nodes in the armpit region to help determine if cancer has spread beyond the breast.Back Flap
A natural tissue flap used for breast reconstruction. LD and TDAP flaps are back flap procedures that take tissue from the upper back region.
Benign
Meaning noncancerous. A benign tumor does not contain cancer cells.
BIA-ALCL
See Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma.
Biopsy
A sample of tissue or fluid that is removed from the body for examination, often to determine if it contains cancerous cells.
Breast Implant Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL)
A rare type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (cancer of the immune system) associated with the use of certain textured implants.
Breast Conservation Surgery
Breast Augmentation
A procedure that enlarges the size of your breast through use of an implant and sometimes fat grafting.
Breast Lift
Also known as mastopexy. A procedure that raises the breast higher on the chest wall.
Breast Prosthesis
A form added to the pocket of a post-surgical bra for women who do not have breast reconstruction after a mastectomy. A prosthesis creates a symmetrical appearance and helps balance the body.
Breast Reduction
Also known as mammaplasty. A procedure that reduces the size of your breast.
BRCA1 and BRCA2
Genes that, when mutated, are associated with an elevated hereditary risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer. People with mutated BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes are at a higher lifetime risk than the general population.
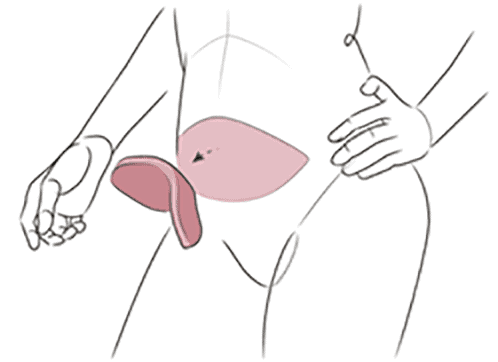
Buttock Flap
A natural tissue flap used for breast reconstruction. SGAP and IGAP flaps are buttock flap procedures that take tissue from the upper buttock and lower buttock, respectively.
Capsular Contracture
Tightening of scar tissue around an implant that can distort the implant’s shape and cause discomfort. It can also make the breast rise higher on the chest.
Chemotherapy
Non-surgical treatment for cancer that uses medication to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing them or by stopping them from dividing.
Combination Reconstruction
DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ)
Cancer cells that have developed in the milk ducts of the breast but have not passed through the duct walls and into nearby tissue. This type of breast cancer is highly curable.
Delayed Breast Reconstruction
Reconstructive surgery that is delayed until after breast cancer treatment and surgery to remove the tumor (mastectomy or lumpectomy) is complete.
DIEP Flap (Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator)
A type of breast reconstruction that uses tissue and fat from the lower abdomen to rebuild the breast. A free flap containing skin, fat, and blood vessels is removed from the abdomen (leaving the abdominal muscles intact) and relocated to the chest to form a new breast.
Direct-To-Implant (DTI)
Reconstruction using implants that immediately reconstructs a breast at the time of mastectomy without the use of a tissue expander.
Donor Site
The place on your body where tissue is removed to reconstruct a breast. Common donor sites include the abdomen, back, buttocks, lumbar, and thigh.
Enhanced Recovery Program (ERP)
A postsurgical protocol designed to improve patient outcomes. The ERP breast reconstruction protocol pioneered by Friedman Center physicians reduces hospital time, decreases pain, and minimizes opioid use.
Exchange Surgery
A surgical procedure in which the tissue expander is removed and replaced with a permanent implant or flap.
Fat Grafting
Also known as lipofilling. Using fat from other parts of your body to improve aesthetic appearance after reconstruction or to create symmetry on the opposite breast. Fat grafting is often used over an implant to give the breast a more natural look and feel.
Fat Necrosis
Dead or damaged breast tissue that can result after breast surgery, radiation, or another trauma.
Flap
A portion of tissue, including skin, fat, and occasionally muscle, that can be taken from different parts of your body and used to reconstruct a breast after surgery.
Flap Reconstruction
See Natural Tissue Reconstruction.
Free Flap
A tissue flap that is completely separated from its original location on your body (donor site) and transplanted using microsurgery to recreate a breast.
Genetic
Relating to genes or heredity.
Genetic Mutations
Permanent changes to the DNA sequence of a gene. This altered gene may be passed down hereditarily.
Going Flat
Choosing not to have reconstructive breast surgery following a mastectomy. Women who go flat should still consult with a plastic surgeon to understand their options.
Hormone Therapy
A cancer treatment that uses drugs to add, block, or remove hormones from your body in order to slow or stop the spread of cancerous cells.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Employing the use of estrogen and progesterone from an outside source because the body’s production of these hormones has decreased. HRT is often used to treat symptoms associated with menopause.
Hybrid Reconstruction
There are two main types of Hybrid Reconstruction. The first known as HyFIL® uses both a small implant and natural tissue to reconstruct a breast. The second is known as HyPad™, uses natural tissue and acellular dermal matrix (ADM) to reconstruct a breast.
Both of these methods can be a good option for thin patients who prefer natural tissue (flap) reconstruction but who do not have enough tissue to recreate their breast(s).
IGAP Flap (Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator)
A type of buttock flap procedure that uses tissue from the base of the buttock to recreate a breast.
Immediate Breast Reconstruction
Reconstructive surgery that happens at the same time as breast cancer surgery to remove a tumor (mastectomy).
Immune System
A complex bodily system used to defend against infection by germs, viruses, and bacteria; also responsible for rejecting transplanted organs or tissues.
Immunotherapy
A cancer treatment that uses drugs to stimulate the immune system to recognize cancer cells as a foreign body and attack these cancer cells.
Implant Reconstruction
Implant Reconstruction uses silicone shells filled with saline (salt water) or silicone gel to recreate a breast. This is in contrast to Flap Reconstruction, which uses tissue from your own body to rebuild a breast.
Implant Replacement
A procedure in which the implants are changed out for a newer model.
Inguinal Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes located in the groin region.
Jackson-Pratt (JP) Drain
LAP Flap (Lumbar Artery Perforator)
A type of lumbar flap procedure that uses tissue from the waist and lower back or “love handle” area to recreate a breast.
LCIS (Lobular Carcinoma In Situ)
A rare condition that occurs when abnormal cells develop in the breast’s milk glands. A diagnosis of LCIS puts you at an elevated risk of developing breast cancer.
LD Flap (Latissimus Dorsi)
A type of pedicled back flap procedure that tunnels skin, fat, and muscle from below the shoulder blade to the chest to recreate a breast.
Lipofilling
Liposuction
A procedure that removes excess fat to slim and reshape areas of the body and improve body contours. Often used in breast reconstruction to improve outcomes.
Lobule
A breast gland that produces milk.
Local Recurrence
The reappearance of cancer at the site of the original tumor.
Lumbar Flap
A natural tissue flap used for breast reconstruction. The LAP flap is a lumbar flap procedure that takes tissue from the waist and lower back.
Lumpectomy
Also known as Breast Conservation Surgery and Partial Mastectomy. Surgery that only removes the portion of the breast with a cancerous tumor along with an adequate margin of normal/healthy tissue.
LYMPHA (Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventative Healing Approach)
Also known as lymphovenous bypass. A cutting-edge, risk-reducing surgical technique performed at the time of breast surgery to help prevent lymphedema.
Lymphatic Surgery
Procedures that relate to the lymphatic system, especially lymph nodes in the armpit region. Lymphatic surgeries include sentinel node biopsy, axillary dissection, and LYMPHA.
Lymphatic System
Small vessels, called lymphatics, that carry lymph fluid all around the body.
Lymphedema
Chronic swelling caused by the removal of the lymph nodes and blocked lymphatics in the armpit region as part of breast cancer treatment.
Margin
The edge of the tissue removed during surgery.
Malignant
Meaning cancerous. A malignant tumor contains cancer cells.
Mammogram
An x-ray screening test for breast cancer.
Mastectomy
Surgical removal of all or part of a breast. Mastectomies can be done to treat existing breast cancer or as a preventive measure. There are several different types of mastectomy: skin-sparing, nipple-sparing, total or simple, modified radical, radical, and partial (lumpectomy).
Mastopexy
Metastasis
The spread of breast cancer cells to another organ.
Microsurgery
An advanced surgical technique, used in some natural tissue reconstruction, to connect very small blood vessels in the tissue flap from the donor site to the chest.
Modified Radical Mastectomy
Breast cancer surgery that removes the entire breast, including the nipple, areola, and excess skin, as well as underarm lymph nodes.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
A diagnostic test that uses a powerful magnet and radio waves to detect cancer.
Multidisciplinary Team
A group of physicians involved in your cancer care, such as a medical oncologist, radiation oncologist, surgical oncologist (breast surgeon) gynecologist, plastic surgeon, genetic counselor, nurse navigator, physical therapist, etc.
Natural Tissue Reconstruction
Also known as Flap Reconstruction and Autologous Tissue Reconstruction. Natural tissue reconstruction uses tissue from another part of your body (donor site) to form a new breast.
Necrosis
Tissue death resulting from a lack of blood supply.
Neoadjuvant Therapy
Cancer treatment, such as radiation or chemotherapy, that is given before breast surgery (lumpectomy or mastectomy).
Nipple and Areola Prosthetics
Temporary, removable replicas that simulate the look and feel of a real nipple and areola.
Nipple and Areola Reconstruction
Surgery that uses the skin of the breast or another area of the body such as the inner thigh, stomach or buttock to surgically form a nipple and areola. Typically done 3-4 months after the breast mound has been created.
Nipple and Areola Tattooing
Specialized medical tattooing that recreates the color of the nipple and areola. Advanced 3D nipple tattooing can provide the illusion of nipple projection on flat skin.
Nipple Sparing Mastectomy
Breast cancer surgery that removes breast tissue but preserves the nipple, areola, and skin of the breast.
Oncologist
A doctor who specializes in the treatment of cancer.
Oncoplastic Surgery
Lumpectomy or partial mastectomy cancer tumor removal and partial breast reconstruction surgery techniques performed at the same time as breast conservation surgery.
PAP Flap (Profunda Artery Perforator)
A type of thigh flap procedure that uses the upper inner portion of the thigh as well as the back of the thigh to create a new breast.
Partial Breast Reconstruction
Procedure(s) done to correct breast defects and restore symmetry following a lumpectomy.
Partial Mastectomy
Pectoralis Muscle
The muscle that stretches across the chest, from the lower shoulder to the breastbone in the center of the chest.
Pedicled Flap
A tissue flap that is tunneled from the donor site under the skin to form a breast. Some of the tissue used to recreate the breast is still attached to the donor site.
Plastic Surgeon
A doctor who performs cosmetic and reconstructive surgeries to shape or alter part of the body’s appearance.
Postsurgical Bra
A supportive bra specially designed for women who have had breast surgery. They typically include pockets to hold a breast prosthesis if needed, but may also be used after breast reconstruction.
Prepectoral Placement
Placement of a breast implant or tissue expander on top of the pectoralis (chest wall) muscle.
Prophylactic or Preventive Mastectomy
Ptosis
Sagging or drooping of the breast skin. Causes of ptosis include aging, weight gain, pregnancy, and breastfeeding.
Pulmonary Embolism
A condition that occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the lung.
Radiation Oncologist
A doctor who oversees and interprets imaging studies such as mammograms, MRIs, bone scans, and CT scans to diagnose disease.
Radiation Treatment
Also known as radiotherapy. A non-surgical treatment that kills cancer cells. Radiation may affect the timing of your breast reconstruction.
Radical Mastectomy
Breast cancer surgery that removes the entire breast, including nipple, areola, and excess skin, as well as underarm lymph nodes. The area removed is larger than in a modified radical mastectomy.
Radiologist
A physician who reads and interprets imaging studies.
Recurrence
A return of cancer after initial treatment.
Retropectoral (Subpectoral) Placement
Placement of a breast implant or tissue expander below the pectoralis (chest wall) muscle.
Revision Surgery
Reconstruction surgery for women who have already had a breast reconstruction. Usually done to improve aesthetic outcomes, replace implants, and/or move from implant to natural tissue reconstruction.
Rippling
Waves or folds that appear on the breast skin when an implant is not covered by adequate tissue.
Risk-Reducing Mastectomy
Also known as prophylactic or preventative mastectomy. Surgery that removes the breast tissue for women who are at high risk of developing breast cancer during their lifetimes (BRCA1/BRCA2 and other associated genetic mutation carriers; LCIS diagnosis).
Round Implant
A type of breast implant that is spherical and usually smooth in texture, creating fullness at the top of the breast.
Saline Implant
A type of breast implant filled with salt water.
Scar Management
Steps that can be taken after breast surgery to promote healing and minimize scarring.
Sentinel Node
The first in a chain of lymph nodes in the axilla (armpit) region.
Sentinel Node Biopsy
A surgical procedure done to establish whether breast cancer has spread into the lymph nodes.
SGAP Flap (Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator)
A type of buttock flap procedure that uses tissue from the top of the buttock to recreate a breast.
SIEA Flap (Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery)
A type of breast reconstruction that uses abdominal tissue and fat from the lower abdomen to reconstruct the breast, while leaving the abdominal muscles undisturbed. The SIEA flap uses vessels that lie just below the skin (in contrast to the deeper vessels used in a DIEP flap), and is only considered when a DIEP flap cannot be performed.
Silicone Implant
A type of breast implant filled with silicone gel.
Simple Mastectomy
Skin-Sparing Mastectomy
Breast cancer surgery that removes the nipple, areola, and breast tissue but preserves the skin of the breast.
Stacked Flap
A type of natural tissue reconstruction that “stacks” two flaps one on top of another to recreate a breast. Stacked flaps may use any common tissue donor site but are most often created from abdominal tissue (stacked DIEP) or a combination of donor sites such as the thigh (stacked PAP). A stacked flap is a good option for women who do not have enough fatty tissue for standard single flap natural tissue reconstruction.
Stage 2 Reconstruction
Also known as second stage procedures. These procedures are part of breast reconstruction but are done after the initial removal of the tumor (mastectomy or lumpectomy) and possibly after initial reconstruction surgery. Stage 2 procedures can include nipple reconstructive surgeries, scar revision, and implant reconstruction following the use of a tissue expander.
Subcutaneous
Beneath the skin.
Subpectoral Placement
Surgical Drain
Also known as Jackson-Pratt or JP drains. Surgical drains (plastic bulbs attached to tubing) are placed at your surgical sites to collect fluid and prevent build-up after breast reconstruction surgery. You will need to empty your drains and record the drainage during recovery.
Surveillance
Conducting regular tests and monitoring your condition to observe any signs of cancer.
Targeted Therapy
A form of cancer treatment that uses drugs to specifically target attacking cancer cells without killing the normal cells.
TDAP Flap (Thoracodorsal Artery Perforator
A type of pedicled back flap procedure used for partial reconstruction after lumpectomy that preserves the latissimus dorsi muscle while using tissue from just beneath the shoulder blade to recreate a breast or correct deficiencies.
Teardrop Implant
A type of breast implant that is larger at the bottom than at the top, creating a more natural or “anatomical” breast. Teardrop implants are usually filled with silicone.
Thigh Flap
A natural tissue flap used for breast reconstruction. PAP, TUG, VUG, and DUG flaps are thigh flap procedures.
Tissue Expander
An adjustable implant used to stretch the skin and prepare the breast for a permanent implant.
Total Mastectomy
Breast cancer surgery that removes the entire breast, including the nipple, areola, and excess skin.
TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominus)
An abdominal flap procedure that uses tissue and muscle to recreate a breast. TRAM flaps can be performed as a free flap or pedicled flap. TRAM flaps are only used in patients who are not candidates for less invasive, muscle-sparing procedures such as the DIEP flap.
TUG/VUG/DUG Flaps (Transverse Upper Gracilis/Vertical Upper Gracilis/Diagonal Upper Gracilis)
Thigh flap procedures that use different parts of the gracilis muscle to recreate a breast.
Tumor
An abnormal mass of tissue.
Ultrasound
A test that uses high-frequency sound waves to generate images. An ultrasound helps diagnose breast cancer and determine if a lump is benign or malignant.
Venous Thromboembolism
A condition that causes a blood clot to form in the veins, often in the legs, arms, or groin. The clot travels throughout the body through the circulatory system, finally lodging in the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism.