About Breast Reconstruction » Implant Procedures » Direct to Implant Procedure
Direct to Implant (DTI) Procedure
On this page

On this page
Direct to implant reconstruction can only be done if there is enough healthy skin at the breast site to contain the volume of the new breast. It may also be done if you prefer a smaller breast so that a large amount of skin isn’t required. Additional enhancement procedures such as fat grafting may be required to optimize the best aesthetic outcome.
Procedure
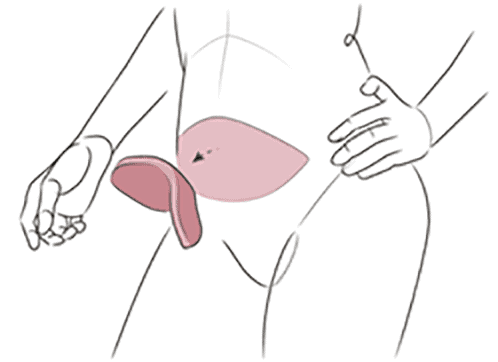
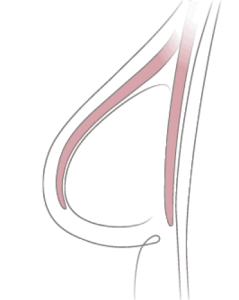
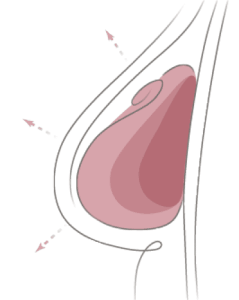
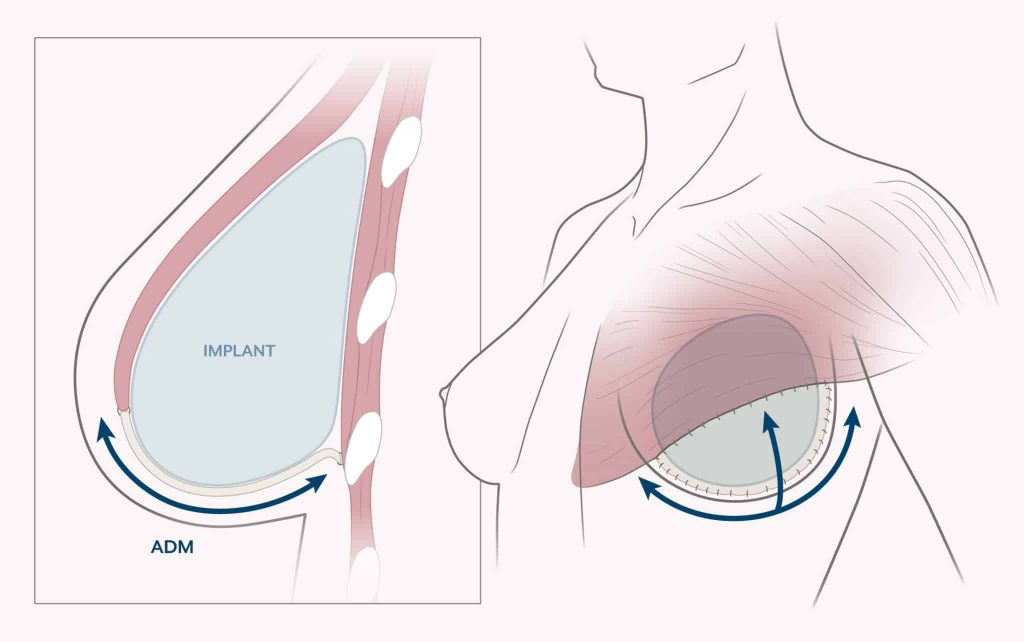
In DTI reconstruction, the implant is put in just after the mastectomy is performed. No tissue expander is used. To hold the implant in place, a sling made out of purified collagen, called acellular dermal matrix (ADM), may be used. The ADM provides a meshlike framework that gives additional support to the implant.
With DTI reconstruction, the volume and shape of your breast is restored immediately—you don’t have to wait for a later surgery. Because most mastectomies are skin-sparing, your own skin can usually be used to contain the implant, enhancing the appearance of the reconstructed breast. And having immediate reconstruction means there’s one less surgery for you to go through.
Recovery Time
Recovery time for implant reconstruction is usually shorter than that for flap reconstruction. You’ll probably be able to return to your typical activities in about 4-6 weeks.
Additional Procedures
- Fat grafting may be performed as a stage two reconstruction procedure to help fill and contour the breast and achieve optimal results.
- If you’re having nipple and aerola reconstruction, that procedure generally happens 3-4 months after placement of your permanent implant.
- Breast implants don’t last forever. Both saline and silicone implants typically need to be replaced in 10-20 years.
Things to Consider
- DTI reconstruction can only be done if there is enough healthy skin at the breast site to contain the volume of the new breast.
- DTI reconstruction often works best for women who prefer a smaller breast, so that a large amount of skin isn’t required. It may be difficult to create a larger breast.
- The immediate insertion of the implant may compromise the breast skin. If the skin is compromised, the implant may be exposed or contaminated and may require removal.
- Secondary procedures, such as fat grafting, or corrective procedures may be more common with DTI reconstruction.
Patient selection is critical in this type of breast reconstruction, so it’s very important to talk with your surgeon and find out if you’re a good candidate for DTI reconstruction.
Additional Choices and Alternatives
Timing of your implant procedures is an important consideration in breast reconstruction. If your implant reconstruction requires tissue expanders, implant placement will be delayed by several months.
You and your surgeon will also need to determine whether implants should be placed above the pectoral (chest wall) muscle or below it.
If you want to combine breast implants with a natural tissue procedure, you may be a candidate for hybrid reconstruction. And if you’re concerned about having to replace implants due to complications or aging, then a natural tissue procedure such as the DIEP flap may be a better choice.